




Types of Simulation
Mixed Simulations
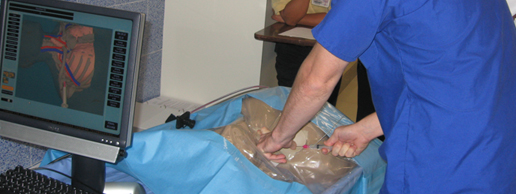
Mixed simulations combine physical and virtual components. For example, virtual information or graphics may be precisely overlaid over a physical component or interposed between a viewer and the physical component. Examples are a Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome and an Augmented Apollo workstation simulation.
Physical Simulations
Physical simulations are tangible physical devices or systems that can be touched and directly manipulated. Examples are mannequin patient simulators such as the UF-invented Human Patient Simulator and part task trainers such as intubation heads.
Standardized Patients
Standardized patients are human actors who are trained to mimic the symptoms of certain conditions. Trainees interact with the standardized patients via natural language and touch.
Virtual Humans
Virtual humans or virtual patients are avatars that are programmed to represent a patient. Interaction is via natural language and pointing. Virtual humans facilitate the representation of rare patients or pathologies.
Virtual Simulations
Virtual simulations are implemented virtually, usually through a display device. There are many different types of virtual simulations. A given virtual simulation can fall into more than one of the categories below.
Transparent Reality Simulations
Transparent reality simulations make the internal, hidden or invisible structure, processes or functions of a system explicit, visible and interactive. A prime example is the Virtual Anesthesia Machine simulation.
Web-enabled Simulations
Web-enabled simulations are accessed via the web through a web browser and will work on both Windows and Mac personal computers. A set of web-enabled simulations can be accessed at the Virtual Anesthesia Machine simulation portfolio.
Photo Realistic Simulations
Photorealistic simulations use photographic quality images for its graphics instead of iconic representations. An example of an interactive photorealistic simulation is the Opaque “Blackbox” VAM simulation.
Panoramic Simulations
Panoramic simulations “stitch” together a set of photographs of a clinical care area such as an operating room to form a 360 degrees background to the simulation. An example is the Simulated Anesthesia Application distributed by Schering Plough.
